Genetic and Clinical Background:
The clinical outcome of Core Binding Factor Leukemia (CBFL) seems influenced by the mutational status of KIT. In fact, several retrospective studies, in addition to our own, as well as a systematic review, indicate that KIT mutations have a negative prognostic impact in AML with t(8;21) or, to a lesser extent, with inv(16)/t(16;16).
In addition, gene expression studies found KIT to be highly expressed in CBFL regardless of its mutational status. Furthermore, recent studies have identified novel recurrent somatic mutations co-occurring with KITmut.
In-vitro studies revealed that Midostaurin (Mido) is effective in inhibiting both wild type (WT) and a range of KIT mutants. In addition, it is proven to be effective in KIT-positive malignancies such as Aggressive Systemic Mastocytosis (ASM), Mast Cell Leukemia (MCL), and SM with Associated Hematological Neoplasm (SM-AHN).
With this background, we designed a Phase II trial to evaluate the safety and efficacy of Mido in association with Intensive Chemotherapy (IC), in CBFL regardless of KIT mutational status.
Methods:
The inclusion criteria were the following: age 18 to 60 years, diagnosis of de-novo CBFL, adequate organ function, signed informed consent. The exclusion criteria were: central nervous system involvement, uncontrolled infections, other active malignancies, a Qtc value greater than 470 ms (according to Bazett formula) at the electrocardiogram, significant uncontrolled or active cardiovascular diseases.
Patients received standard induction therapy with an anthracycline containing regimen ("7+3"-like) + Mido, three cycles of post-remission consolidation chemotherapy with high-dose cytarabine + Mido, and 12 months of Mido as Maintenance.
The Mido dosage was: 50 mg orally twice a day, on days 8-21, in association with IC, and 50 mg orally twice a day as single agent maintenance.
In order to attain a reduction in 2 years Relapse Incidence (RI), from the historical value of 48% to 28% (Primary Objective of the Study), we plan to enrol 39 patients (power 82%, alpha error 4,6%). At diagnosis all patients were studied by a comprehensive NGS panel targeting 40 DNA genes and 29 RNA fusion driver genes. MRD status was assessed by qPCR and high-resolution multicolor flow cytometry at established check-points during consolidation and maintenance therapy.
Results:
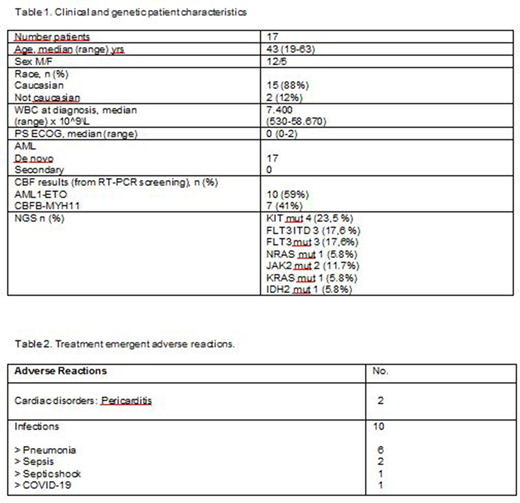
17 patients were enrolled between December 2018 to April 2020 (table1). Overall, the CR rate was 94.2%. At a median follow-up of 9 months (range 3-19 months), we recorded a RI of 12.5%, an OS of 93.7%, and a DFS of 81.2%. 16 patients continue on study and 14 patients are in 1st CR, MRD-negative by flow cytometry and qPCR.
Six patients (35.2 %) experienced 12 Treatment Emergent Adverse Event (TEAE), 10 out of whom were infections, with grade 3-4 neutropenia (Table 2). We only recorded one death from SARS-Cov2 infection (Interstitial Pneumonia) in a patient in MRD-negative complete remission. There were no treatment-related deaths.
Conclusion:
In patients with CBFL, the regimen consisting of intensive chemotherapy and consolidation chemotherapy in association with Mido, followed by Mido maintenance, had an acceptable safety profile and excellent response rates with a significant proportion of patients in MRD-negative complete remission. Trial is continuing to accrue (EudraCT Number 2017-002094-18; ClinicalTrials ID: NCT 03686345). This work was supported by a grant from Fondazione Regionale per la Ricerca Biomedica (FRRB 2015).
Krampera:Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Todisco:Jannsen, Abbvie, Jazz: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Veronese:Novartis: Other: Travel Expenses; Bayer: Honoraria; AstraZeneca: Other: Travel Expenses; Janssen Cilag: Honoraria.
Midostaurin for treatment of Core Binding Factor Leukemia. The drug has been used as KIT inhibitor.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal